Website indexing is an initial step (post-crawling) in how webpages are positioned and offered as outcomes within search engine results. It forms a crucial stage (following crawling) in a complex process that enfolds comprehending webpage content for subsequent ranking and presentation in search engine findings.
Search engines persistently refine their methods for exploring and indexing web domains.
For technical SEO, gaining insights into Google’s and Bing’s methodologies for exploring and indexing websites is required. It is instrumental in developing approaches to enhance search performance.

How Does a Search Engine Work for Web Indexing?
Website Indexing in search engines starts the ranking procedures after a website crawling.
Indexing fundamentally is a process where a webpage’s content documents Google’s database for potential ranking.
When creating a new page on your site, several options exist to index it on Google.
The most straightforward technique for a page’s indexing is to do nothing.
Google’s crawlers trace links. Hence, assuming your site is already within the index and the fresh content is linked within your site, Google will ultimately crawl it and add it to its index. More details on this will be explained subsequently.

How to Index a Page Faster?
But how can you make sure Googlebot reaches your page quickly?
This is crucial when your content is time-sensitive or if you’ve made a significant update to a page that you want Google to be aware of.
I prefer quicker techniques when I’ve enhanced an important page or modified the title and description to boost clicks.
I’m curious about when they were found and displayed in search results, which helps me track the starting point of the improvement.
In these cases, there are a couple of extra methods you can apply for efficient website indexing.
1.Website Indexing With Google Search Console
In Search Console, there’s a useful option called “Request Indexing” which is all about website indexing.
To use it, start by clicking the search box at the top. It might say something like “Inspect and URL in domain.com.”
Type in the web address you want to get noticed by search engines, then press Enter.
If Google is already familiar with that page through website indexing, you’ll see a bunch of info. Don’t worry about that now, but if you haven’t looked before, it’s a good idea to check it out. For our focus here, the important part is a button that’s helpful whether Google knows the page or not due to website indexing. This button is great for making sure Google spots new stuff or understanding recent changes.
Look for the button shown below. In just a little while, you can search for new content or URLs on Google and see that your changes or new content have been found, thanks to the power of website indexing.
2.XML Sitemaps
XML sitemaps serve as a pretty old but reliable way to get a search engine’s attention for your website’s content. They’re like a list that tells search engines about all your site’s pages and some extra details, like when they were last changed.
You can send this list (sitemap) to Bing using Bing Webmaster Tools, and also to Google through Search Console.
It’s a good move, especially if you want to make sure search engines know about your site.
But, if you’re in a hurry to make a page appear in search results quickly, using sitemaps might not always work as reliably as you hope.
International Business Development Services by Bizkook:
- International Branding and Strategy Consultation
- International Business Development Consultation
- International Branch Expansion
- Organizing International Exhibitions and Business Tours
- And more…
3.Bing’s IndexNow for Website Indexing
Bing has introduced a new method called IndexNow to enhance website indexing. It helps search engines locate and update new or modified content more efficiently. With IndexNow, search engines are alerted about fresh or updated content, prompting them to include it in search results swiftly.
This innovative approach, called a “push” method, sends information to search engines. This is in contrast to the traditional “pull” method, where search engine crawlers decide when to visit and index content.
The advantage of IndexNow extends to resource efficiency for web hosting and data centers. This is environmentally friendly and conserves bandwidth. Significantly, it accelerates the process of getting content indexed in search results.
Presently, Bing and Yandex employ IndexNow. Implementation is straightforward, with available plugins for popular platforms such as WordPress and Drupal. IndexNow is also supported by services like Cloudflare and Akamai, making it widely accessible for enhancing website indexing.

4.Bing Webmaster Tools Another Way Of Indexing Website
When focusing on website indexing, you should also think about having a Bing Webmaster Tools account.
If you haven’t got one yet, I really suggest you do. It’s not just about website indexing.
The info it provides is big and can help you figure out problems and make your rankings better on Bing, Google, and other places – which will probably make things better for users too. But to get your stuff listed through website indexing, you just need to click: Set Up My Site > Share Links.
Type in the website addresses you want to get listed through website indexing and press “Share.” So, that’s mostly what you need to know about website indexing and how search engines handle website indexing. There’s also a Bing Webmaster Tools Indexing API that can speed up how quickly your content shows up in Bing’s search results through website indexing, sometimes even within hours.
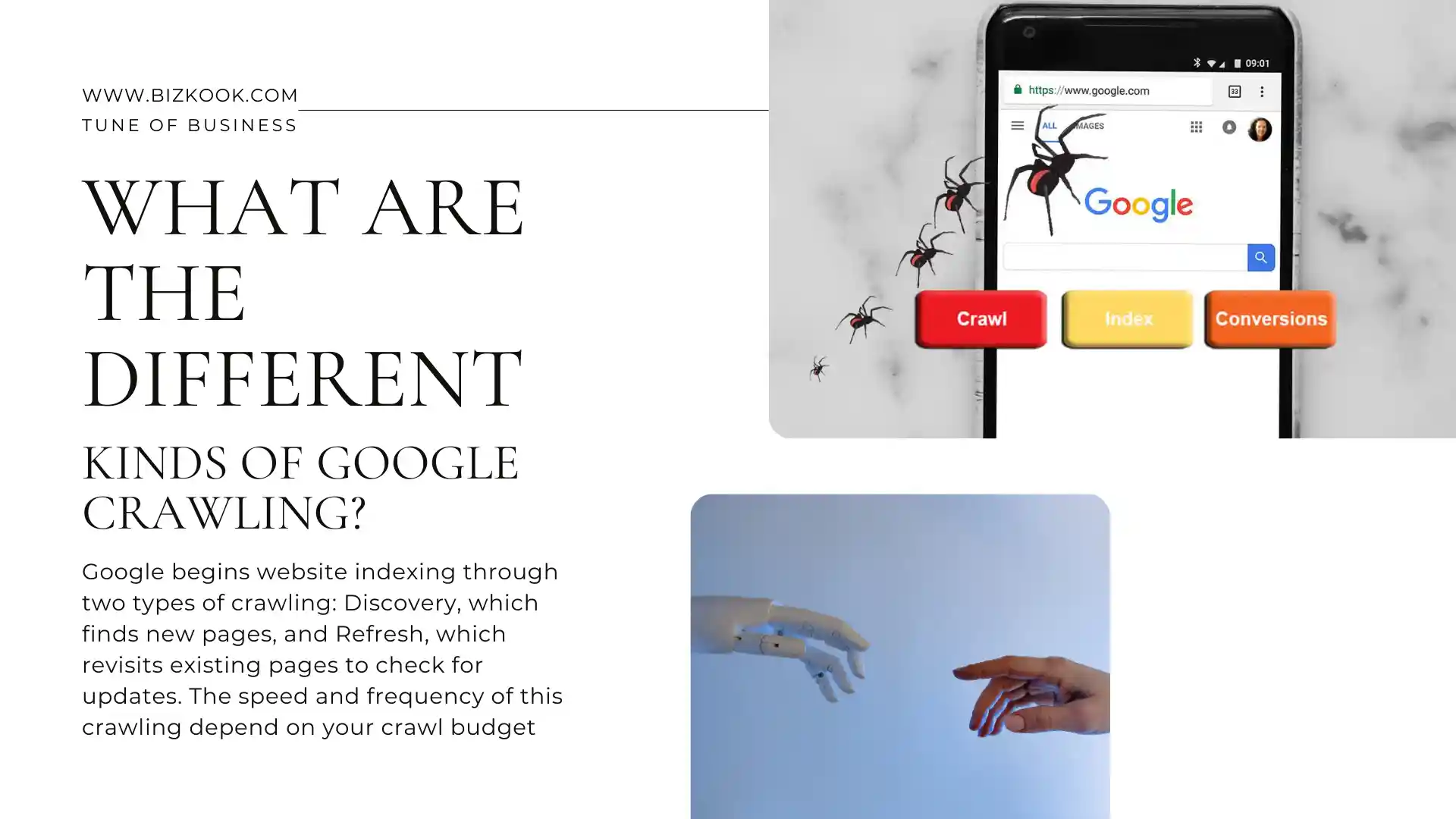
What are the different kinds of Google crawling?
Google’s process of website indexing starts with crawling, which comes in two forms: Discovery and Refresh. Discovery is when Google finds new web pages to include in its index. Refresh, on the other hand, is when Google identifies changes in web pages that it has already added to its index.

What is Crawl Budget?
To discuss website indexing, we need to understand the crawl budget. The crawl budget is like the resources Google uses to explore a website.
This budget depends on two main things:
- How fast your server is (how much Google can explore without making your website slow for users).
- How important your site is. For example, a big news site with always changing content gets explored often. But if you have a small local shop website with a few links, it’s not explored as much.
You can learn more about crawl budgets and how they work from Google’s explanation.

How Google And Other Search Engines Work?
Making sure your website is seen on search engines like Google starts with having good content and getting it recognized through a process called “website indexing.” Think of it as your content’s journey to the top of search results.
To begin, search engines like Google use special tools to explore web pages and gather information about them. This is called “crawling.” After that, they add the collected information to their databases, which is the “indexing” part. It’s like organizing a library of web pages.
When someone searches for something on Google, the search engine uses its index to find the most relevant pages. The pages are then ranked based on different factors, like how useful and trustworthy they seem.
Over time, search engines have become really smart. They can even answer questions directly on the search results page and show different types of content. They’re always changing to make searches better.
In 2020, Google did a lot of experiments to improve how searches work. They test new features to see if they’re helpful before releasing them to everyone.
Knowing how these processes work can help your content get noticed by Google. It’ll also help you understand the results you see when you search for things online.





